짜증나는 Restdoc 템플릿을 조금 더 편하게 작성하자
java
짜증나는 Restdoc
회사에서 org.springframework.restdocs을 쓰고 있어서 처음으로 Restdoc을 쓰게 되었다.
그런데 request, response 용 json 스키마를 만드는 게 너무 귀찮았다.
예를 들어 다음과 같은 request json과, response json이 있다고 하자.
- request json
{
"member": {
"id": 3092,
"name": "John Grib",
"favorite": {
"movie": {"name": "Starwars", "star": 5}
}
}
}
- response json
{
"success": true
}
그러면 다음과 같은 restdoc 코드를 작성하게 된다.
resultActions
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(
document("member/profile",
requestFields(
fieldWithPath("member").type(OBJECT).description("회원"),
fieldWithPath("member.id").type(NUMBER).description("회원번호"),
fieldWithPath("member.name").type(STRING).description("이름"),
fieldWithPath("member.favorite").type(OBJECT).description("좋아하는 것들"),
fieldWithPath("member.favorite.movie").type(OBJECT).description("영화"),
fieldWithPath("member.favorite.movie.name").type(STRING).description("영화 이름"),
fieldWithPath("member.favorite.movie.star").type(NUMBER).description("영화 별점")
),
responseFields(
beneathPath("data").withSubsectionId("data"),
fieldWithPath("success").type(BOOLEAN).description("성공여부")
)
));
요청과 응답이 아주 간단해서 그렇지, 조금만 복잡해져도 이 작업은 엄청 짜증난다.
특히 계층 구조로 작업할 수 없다는 점이 답답하다.
jq 명령으로 계층구조 상의 모든 아이템 경로를 출력해 쓰기
물론 터미널에서 [[/cmd/jq]]를 사용해 다음과 같이 모든 아이템까지의 경로를 출력하는 방법이 있긴 하다.
jq -c 'path(..)|[.[]|tostring]|join(".")' request.json
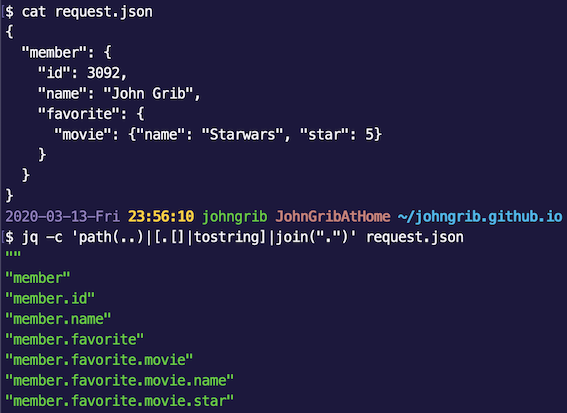
이제 이 결과를 복붙해서 쓰면 된다.
그러나 코드 입력이 조금 편해질 뿐 시각적인 공해는 그대로이다.
FieldDescriptor 리스트 생성기를 만들어 쓰자
그래서 다음과 같은 클래스를 하나 대충 만들어 보았다.
package com.johngrib..web;
import static org.springframework.restdocs.payload.PayloadDocumentation.fieldWithPath;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.restdocs.payload.FieldDescriptor;
import org.springframework.restdocs.payload.JsonFieldType;
public class Item {
String path = "";
JsonFieldType type;
String desc = "";
List<Item> children = new ArrayList<>();
State state = State.NONE;
enum State {
IGNORED,
OPTIONAL,
NONE
}
public Item(String path, JsonFieldType type, String desc, State state, List<Item> children) {
this.path = path;
this.type = type;
this.desc = desc;
this.state = state;
this.children = children;
}
public Item(String path, JsonFieldType type, String desc, State state) {
this.path = path;
this.type = type;
this.desc = desc;
this.state = state;
}
public Item(String path, List<Item> children) {
this.path = path;
this.children = children;
}
static Item of(String path, JsonFieldType type, String desc, State state, Item... children) {
return new Item(path, type, desc, state, Arrays.asList(children));
}
static Item of(String path, JsonFieldType type, String desc, State state) {
return new Item(path, type, desc, state);
}
static Item of(String path, JsonFieldType type, String desc, Item... children) {
return new Item(path, type, desc, State.NONE, Arrays.asList(children));
}
static Item of(String path, JsonFieldType type, String desc) {
return new Item(path, type, desc, State.NONE);
}
static Item of(String path, List<Item> children) {
return new Item(path, children);
}
static Item of(String path, Item... children) {
return new Item(path, Arrays.asList(children));
}
static Item of(Item... children) {
return new Item("", Arrays.asList(children));
}
public FieldDescriptor toField() {
FieldDescriptor f = fieldWithPath(this.path)
.type(this.type)
.description(this.desc);
switch (this.state) {
case IGNORED:
return f.ignored();
case OPTIONAL:
return f.optional();
default:
return f;
}
}
public List<Item> toFlatList(String superPath) {
List<Item> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (superPath != null && !"".equals(superPath)) {
this.path = superPath + "." + this.path;
}
if (this.type != null || this.children == null || this.children.size() < 1) {
list.add(this);
}
for (Item child : children) {
list.addAll(child.toFlatList(this.path)); // 재귀
}
return list;
}
public List<Item> toFlatList() {
return toFlatList("");
}
public List<FieldDescriptor> build() {
List<FieldDescriptor> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Item i : toFlatList()) {
list.add(i.toField());
}
return list;
}
}
이 클래스는 다음과 같이 사용하면 된다.
Item requestItems = Item.of("member", OBJECT, "회원",
Item.of("id", NUMBER, "회원번호"),
Item.of("name", STRING, "이름"),
Item.of("favorite", OBJECT, "좋아하는 것들",
Item.of("movie", OBJECT, "영화",
Item.of("name", STRING, "영화 이름"),
Item.of("star", NUMBER, "영화 별점"))));
Item responseItems = Item.of("success", BOOLEAN, "성공");
resultActions
.andExpect(status().isMultiStatus())
.andDo(
document("member/profile",
requestFields(
beneathPath("data").withSubsectionId("data"),
requestItems.build()
),
responseFields(
beneathPath("data").withSubsectionId("data"),
responseItems.build()
)
));
Item 클래스를 static import하면 다음과 같이 쓸 수도 있다.
// of 에 주목!
Item requestItems = of("member", OBJECT, "회원",
of("id", NUMBER, "회원번호"),
of("name", STRING, "이름"),
of("favorite", OBJECT, "좋아하는 것들",
of("movie", OBJECT, "영화",
of("name", STRING, "영화 이름"),
of("star", NUMBER, "영화 별점"))));
Item responseItems = Item.of("success", BOOLEAN, "성공");
resultActions
.andExpect(status().isMultiStatus())
.andDo(
document("member/profile",
requestFields(
beneathPath("data").withSubsectionId("data"),
requestItems.build()
),
responseFields(
beneathPath("data").withSubsectionId("data"),
responseItems.build()
)
));
before, after 비교
- before
fieldWithPath("member").type(OBJECT).description("회원"),
fieldWithPath("member.id").type(NUMBER).description("회원번호"),
fieldWithPath("member.name").type(STRING).description("이름"),
fieldWithPath("member.favorite").type(OBJECT).description("좋아하는 것들"),
fieldWithPath("member.favorite.movie").type(OBJECT).description("영화"),
fieldWithPath("member.favorite.movie.name").type(STRING).description("영화 이름"),
fieldWithPath("member.favorite.movie.star").type(NUMBER).description("영화 별점")
- after
of("member", OBJECT, "회원",
of("id", NUMBER, "회원번호"),
of("name", STRING, "이름"),
of("favorite", OBJECT, "좋아하는 것들",
of("movie", OBJECT, "영화",
of("name", STRING, "영화 이름"),
of("star", NUMBER, "영화 별점"))));